| |
|
|
CHARACTERIZATION OF POTATO VIRUS Y (PVY)
Potato virus Y (PVY) belongs to the Potyviridae family - the largest
and economically most important group of plant viruses. Potyviruses
are detected in all climatic zones and infect almost all crop plants
and a lot of wild species.
Main method of protection from PVY is breeding resistant cultivars,
so screening for new sources of resistance to PVY as well as screening
isolates acquired from different regions of the world are very important.
Potato isolates have been divided into three main strains: PVYN,
PVYO and PVYC, according to the symptoms induced on tobacco and
potato. Isolates belonging to the PVYN strain induce tobacco veinal
necrosis on Nicotiana tabacum, limitation of ability of assimilation
and gas exchange, inhibition of water and mineral salts transport
to leaves tissue. On the basis of symptoms induced on potato, PVYN
isolates can be divided into two groups: the first one (PVYNW) causes
mild mosaic symptoms in most potato cultivars, the other one provokes
potato tuber necrotic disease, expressed as necrotic rings on tubers
and is referred to as PVYNTN (necrotic tuber necrosis). PVY causes:
yield and dried leaves quality decrease as well as disadvantageous
increase of nitrates level on tobacco leaves. The PVYO strain (common
strain) isolates induce non-necrotic mosaic on tobacco. The PVYC
strain causes stipple streak symptoms on potato cultivars carrying
the Nc resistance gene and non necrotic symptoms, similar to those
of PVYO on Nicotiana tabacum.
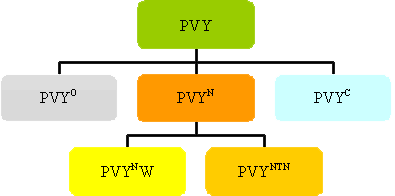
Classification of PVY isolates
The characterization of PVY involves:
Biological tests
- kind of symptoms observation
- evaluation of plants affected by a disease
- PVY isolates evaluation of ability to break of resistance
Serological tests (DAS-ELISA - Double Antibody Sandwich Enzyme
Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
- grouping of collected PVY isolates
- comparison of PVY isolates collected from tobacco
and potato
Molecular characterization (RFLP method and DNA sequencing)
- evaluation of genetic diversity
- phylogeny analysis
|
|
